Acceptance criteria are specific and measurable conditions that must be met for a product, service, or deliverable to be considered acceptable. Acceptance criteria are typically established during the planning stages of a project and are used to ensure that all parties involved have a clear understanding of what is expected.
The acceptance criteria can include requirements related to functionality, performance, usability, reliability, and other factors that are important to the stakeholders. For example, acceptance criteria for air conditioning unit covers located within 1000M of salt water may include an upgrade of powder coating to a minimum 80um.
Acceptance criteria will also be dependent on the characteristic being inspected or tested, typically this would include the results of the specified inspection or test, conformity with the relevant standard or specification. Where this is not evident or available then other means of acceptance criteria can be used, these include but are not limited to:
• Client / certifier / consultant approvals
• Approved workshop drawings
• Technical details
• Samples
• Prototype
• Manufacturers’ recommendations
Using a precast concrete element as a practical example, we can see how a combination of multiple acceptance criteria may be required.
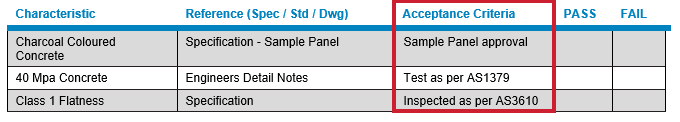
Note This simplified example is not intended to consider all elements for an ITP.
Where an inspection or a test fails to meet the criteria then action is required to address the non-conformance. These actions include the immediate actions taken to deal with the issue as well as other actions to prevent recurrence.
For further information see Corrective Action Report